What Is The Main Principle Of Vsepr
Vsepr theory and shapes of molecules Vsepr molecules chemistry geometry compoundchem molecule electron bonding moleculares revision geometria repulsion valence electrons modelos Vsepr theory
Jimchem: VSEPR Theory
Jimchem: vsepr theory Vsepr theory Solved which statement about vsepr theory is not correct?
Solved vsepr main
Vsepr atoms theory bonded electron molecules least adopt depending uponCompound interest: vsepr & shapes of molecules Theory bond valence vsepr vbt ppt powerpoint presentation bondingDay 11: resonance structures, vsepr theory – chemistry 109.
Vsepr theory transcribedVsepr geometry electron geometria hybridization bonding lone chem classroom ikatan bonds atoms geometrie orbital chemie xe Compound interest: vsepr & shapes of moleculesVsepr theory pair electron repulsion valence.
Vsepr molecules molecular geometry compoundchem molecule compound electron bonding moleculares valence geometria electrons
Jimchem: vsepr theoryDay 11: resonance structures, vsepr theory – chemistry 109 Vsepr & shapes of moleculesSolved 1) what is the main idea behind vsepr theory? 2) for.
Vsepr shapes molecules chemistry compoundchem compound organic level theory chem science teaching ocr lessons molecular bonding poster table bond geometryChemistry electron vsepr polarity chem molecule bonds geometries pyramidal predicting vsper pairs regions bonding predict chemical compounds where simple angles Vsepr pairs atoms bonded bond electron molecules only repulsion least chem adoptElectron pairs vsepr geometries geometry bonding trigonal chem bonds.

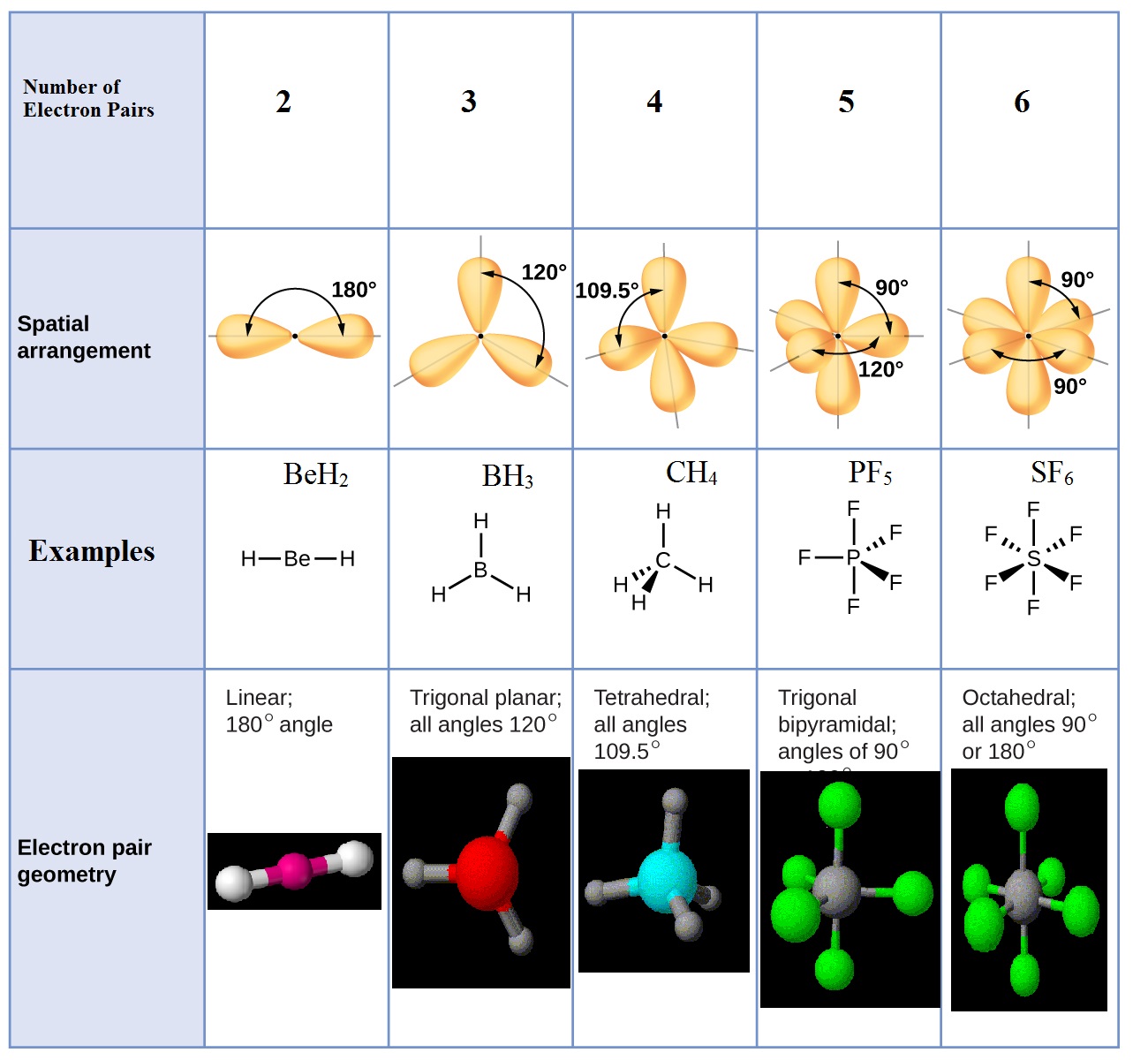
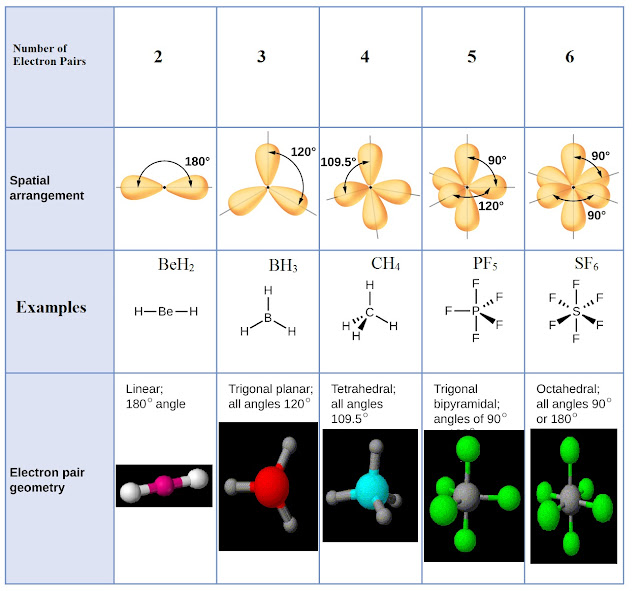
Vsepr theory chart
.
.


VSEPR Theory - Basic Introduction - YouTube
Jimchem: VSEPR Theory

Day 11: Resonance Structures, VSEPR Theory – Chemistry 109
Solved Which statement about VSEPR theory is not correct? | Chegg.com

PPT - VSEPR Theory and Valence bond theory PowerPoint Presentation

Vsepr theory chart

VSEPR Theory and Shapes of Molecules

Day 11: Resonance Structures, VSEPR Theory – Chemistry 109

Solved 1) What is the main idea behind VSEPR theory? 2) For | Chegg.com